Total Hip Replacement (THR), also known as Total Hip Arthroplasty, is a highly successful surgical procedure performed to relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients suffering from severe hip joint damage. Most commonly performed for osteoarthritis, hip replacements are among the most effective and life-enhancing orthopedic procedures available today.
Understanding the Hip Joint
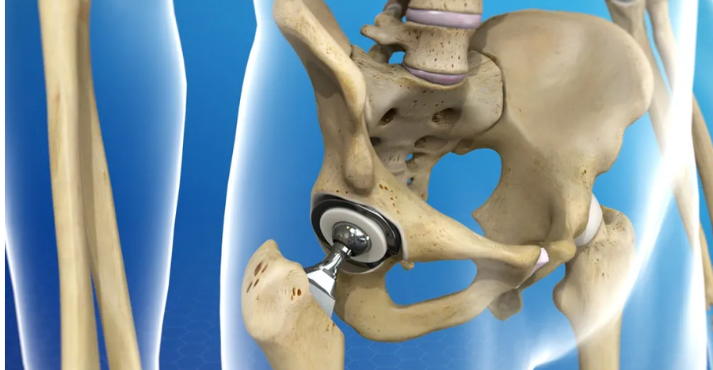
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint where the femoral head (ball) of the thigh bone fits into the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvic bone. It allows smooth, stable movement necessary for walking, bending, sitting, and standing.
In conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, or post-traumatic arthritis, the cartilage that cushions the joint wears away, causing the bones to rub together. This leads to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility—often severely affecting quality of life.
What is Total Hip Replacement?
Total hip replacement involves removing the damaged portions of the hip joint and replacing them with prosthetic components:
- A metal or ceramic ball that replaces the femoral head
- A metal socket inserted into the pelvic bone
- A plastic, ceramic, or metal liner between the two to allow smooth movement
This procedure aims to:
- Eliminate chronic hip pain
- Improve joint function and stability
- Restore mobility and independence
Indications for Hip Replacement
- You may be a candidate for Total Hip Replacement (THR) if you experience:
- Persistent pain despite medications and physiotherapy
- Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily tasks
- Hip stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Sleep disturbances due to hip pain
- Advanced joint damage visible on X-rays or MRI
- Common conditions leading to THR:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Avascular necrosis (loss of blood supply to the femoral head)
- Hip fractures or post-traumatic arthritis
- Congenital or developmental hip disorders
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
- 1.Total Hip Replacement (Conventional)
Replaces both the acetabulum and the femoral head with prosthetic components.
- 2.Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement
Uses smaller incisions, less muscle cutting, and quicker recovery.
- 3. Robotic-Assisted Hip Replacement
Uses advanced technology for precision alignment and optimal implant positioning
- 4. Revision Hip Replacement
A second procedure when the initial implant wears out or fails.
The Procedure
- Performed under spinal or general anesthesia
- Takes 1–2 hours on average
- Involves removing the damaged bone and cartilage and placing the artificial joint components
- Patients typically begin walking within 24–48 hours after surgery with support
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery timelines vary depending on age, general health, and the type of surgery. Key stages include:
- Hospital Stay: 2–5 days (in most cases)
- Early Recovery: Use of walker or crutches, pain management, gentle physiotherapy
- Rehabilitation: Exercises to regain strength, flexibility, and balance
- Return to Activities:
- Basic activities: 2–4 weeks
- Driving: 4–6 weeks
- Low-impact sports: 10–12 weeks
- Full recovery: Up to 3–6 months
Adherence to rehab protocols and precautions (e.g., avoiding extreme hip positions) is essential to ensure long-term success.
Benefits of Total Hip Replacement
- Significant pain relief
- Improved range of motion
- Restoration of walking ability and independence
- Enhanced quality of life
- Long-lasting results (implants typically last 15–25 years or more)
Risks and Considerations
While hip replacement is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Dislocation
- Leg length discrepancy
- Implant wear or loosening over time
With modern techniques and experienced surgeons, complication rates remain low.
Why Choose a Specialist for Hip Replacement?
A skilled orthopedic surgeon, especially one trained in joint replacement and arthroplasty, ensures:
- Accurate implant positioning
- Personalized care plans
- Advanced surgical techniques (robotic, minimally invasive)
- Long-term joint health