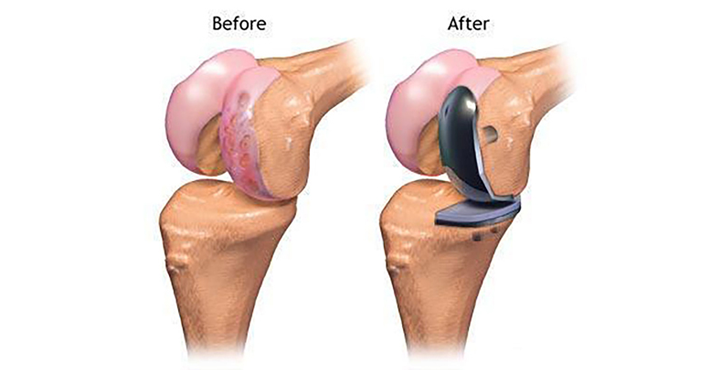
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR), also known as Unicompartmental Knee Replacement, is a surgical procedure that replaces only the damaged part of the knee joint, rather than the entire joint. It is a less invasive alternative to total knee replacement, offering quicker recovery, less pain, and a more natural knee movement.
This procedure is ideal for patients with arthritis limited to a single compartment of the knee—typically the medial (inner), lateral (outer), or patellofemoral (kneecap) area—while the rest of the joint remains healthy.
Understanding the Knee Joint
The knee joint is made up of three compartments:
- Medial compartment – inside part of the knee
- Lateral compartment – outside part of the knee
- Patellofemoral compartment – between the kneecap and femur
In many patients, osteoarthritis affects only one of these compartments. When non-surgical treatments no longer relieve symptoms, partial knee replacement becomes an excellent option for restoring joint function and relieving pain without replacing the entire knee.
Who is a Candidate for Partial Knee Replacement?
Ideal candidates typically:
- Have arthritis confined to one compartment of the knee
- Have intact ligaments (especially the ACL and PCL)
- Experience localized knee pain
- Maintain a reasonable range of motion
- Have not found relief from medications, injections, or physiotherapy
PKR is not recommended for those with:
- Inflammatory arthritis (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis)
- Significant knee deformity
- Ligament instability or extensive joint damage
Benefits of Partial Knee Replacement
- Smaller incision and less bone removal
- Faster recovery and shorter hospital stay
- Reduced pain and swelling after surgery
- Lower risk of blood loss and complications
- More natural knee movement
- Improved function and quality of life
- Easier revision to total knee replacement if needed in the future
The Procedure
- Typically performed under spinal or general anesthesia
- Duration: 1–1.5 hours
- The surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the affected compartment
- An artificial implant (metal and plastic components) is fitted into the cleaned joint space
- The healthy parts of the knee are preserved
Minimally invasive techniques and robotic assistance (if available) can further enhance precision and outcomes.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Hospital Stay: Often just 1–2 days
- Weight Bearing: Most patients walk with support within 24 hours
- Rehabilitation: Starts immediately with physical therapy focused on regaining strength, flexibility, and balance
- Return to Daily Activities:
- Light activities: 2–4 weeks
- Driving: 2–3 weeks
- Full recovery: 6–8 weeks
Patients often report a more "natural" feeling in the knee post-surgery compared to total knee replacements.
Risks and Considerations
Though generally safe, partial knee replacement can involve:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
- Implant wear or loosening
- Disease progression in the other compartments of the knee
- Need for revision surgery (conversion to total knee replacement)
Choosing an experienced knee replacement surgeon significantly reduces these risks and improves outcomes.
Why Choose Partial Knee Replacement?
Partial knee replacement is an excellent option for selected patients looking to maintain a more active lifestyle with:
- Less downtime
- Quicker return to work or sports
- Preservation of more natural joint movement
Many patients find that PKR offers the perfect balance between symptom relief and joint preservation—without undergoing full joint replacement surgery.