Shoulder arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows orthopedic surgeons to diagnose and treat a wide range of shoulder problems with precision and minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. Through small incisions, a tiny camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments are inserted into the joint, enabling high-definition visualization and treatment of structures like tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and bones.
This technique has revolutionized the management of common shoulder injuries, particularly
rotator cuff tears and
shoulder dislocations that require
Bankart repair.
1. Rotator Cuff Repair
The rotator cuff is a group of four tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and enable overhead arm movement. Tears in the rotator cuff are common in athletes, manual laborers, and older adults, typically resulting from:
- Repetitive overhead activity.
- Traumatic injury.
- Degenerative wear and tear over time.
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear:
- Persistent shoulder pain, especially at night
- Weakness when lifting the arm
- Limited range of motion
- Clicking or popping sounds with movement
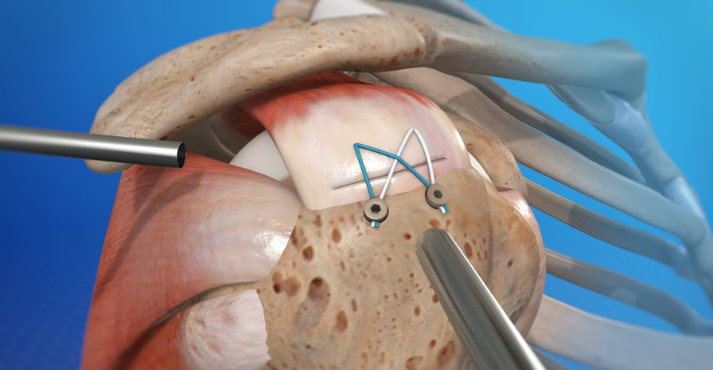
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair involves:
- Debriding (cleaning) the torn tendon edges
- Anchoring the tendon back to the bone using sutures and suture anchors
- Occasionally augmenting the repair with biologic materials in large or complex tears
Benefits of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair:
- Smaller incisions and less tissue trauma
- Reduced pain and scarring
- Faster rehabilitation and return to daily activities
- High success rate in restoring shoulder function
2. Bankart Repair
The Bankart lesion refers to a tear of the labrum (cartilage ring) in the front part of the shoulder socket (glenoid) due to shoulder dislocation. This injury is common in young athletes involved in contact sports or overhead activities like volleyball, tennis, or swimming.
Symptoms of a Bankart lesion:
- Repeated shoulder dislocations
- A sense of instability or the shoulder “slipping out”
- Weakness or apprehension with overhead movements
Arthroscopic Bankart repair includes:
- Reattaching the torn labrum to the glenoid using suture anchors
- Tightening the shoulder capsule (capsular shift) to restore stability
- Preserving joint motion while preventing future dislocations
Advantages of arthroscopic Bankart repair:
- Minimally invasive approach with excellent cosmetic results
- Reduced postoperative pain and faster healing
- Precise repair with high-definition visualization
- Faster return to sports and activities
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Postoperative recovery after shoulder arthroscopy depends on the extent of repair and patient-specific factors. Key phases include:
- Immobilization: Sling usage for 2–6 weeks to allow healing
- Physiotherapy: Starts early with passive motion, progressing to strengthening and sport-specific rehab
- Full recovery:
• Rotator cuff repair: 4–6 months for full function
• Bankart repair: 3–5 months before return to sport
Strict adherence to rehabilitation protocols ensures optimal healing and minimizes the risk of re-injury.
Who Needs Shoulder Arthroscopy?
Ideal candidates include:
- Patients with persistent shoulder pain or weakness not relieved by conservative treatment.
- Athletes or active individuals with shoulder instability.
- People with rotator cuff tears, labral injuries, or impingement syndromes.
- Older adults with degenerative shoulder conditions affecting mobility.